Charles I, King Of Bohemia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Charles IV ( cs, Karel IV.; german: Karl IV.; la, Carolus IV; 14 May 1316 – 29 November 1378''Karl IV''. In: (1960): ''Geschichte in Gestalten'' (''History in figures''), vol. 2: ''F–K''. 38, Frankfurt 1963, p. 294), also known as Charles of Luxembourg, born Wenceslaus (, ), was the first
Charles IV ( cs, Karel IV.; german: Karl IV.; la, Carolus IV; 14 May 1316 – 29 November 1378''Karl IV''. In: (1960): ''Geschichte in Gestalten'' (''History in figures''), vol. 2: ''F–K''. 38, Frankfurt 1963, p. 294), also known as Charles of Luxembourg, born Wenceslaus (, ), was the first
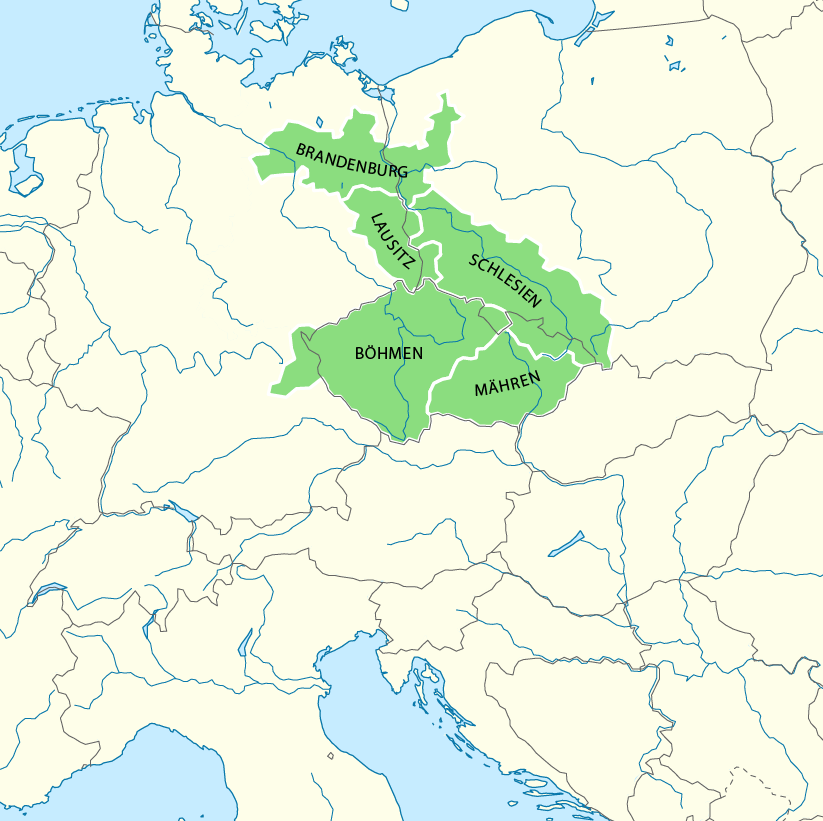 Charles IV was in a very weak position in Germany. Owing to the terms of his election, he was derisively referred to as a "Priests' King" (''Pfaffenkönig''). Many bishops and nearly all of the
Charles IV was in a very weak position in Germany. Owing to the terms of his election, he was derisively referred to as a "Priests' King" (''Pfaffenkönig''). Many bishops and nearly all of the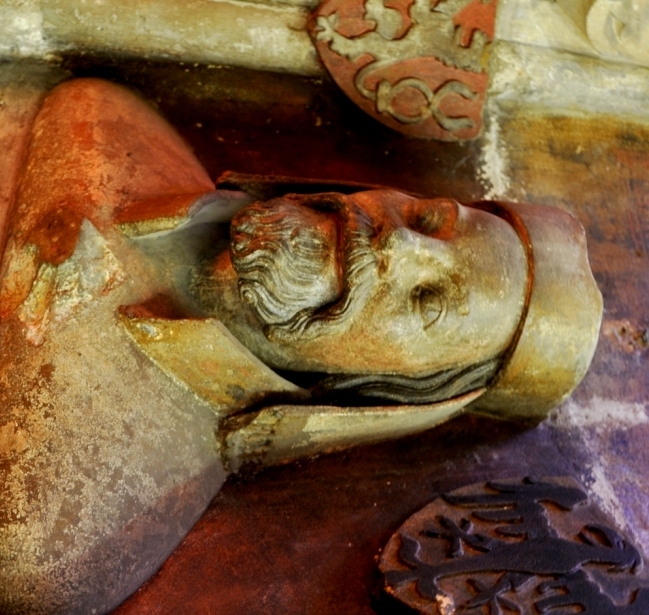  Having made good use of the difficulties of his opponents, Charles was again elected in
Having made good use of the difficulties of his opponents, Charles was again elected in
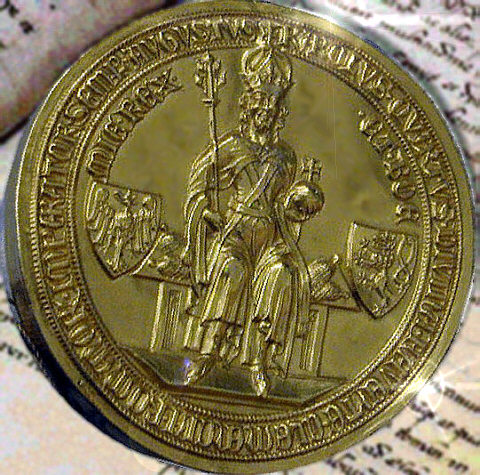 In 1354, Charles crossed the
In 1354, Charles crossed the  Having given
Having given

Karel IV. – český král
/ref> *
 * The 100-
* The 100-
 Charles was married four times. His first wife was
Charles was married four times. His first wife was
books.google.com
*
Entry in the ''Residenzen-Kommission''
Regesta Imperii
Publications on Charles IV.
in the OPAC of the Regesta Imperii
'Constitutiones et acta publica imperatorum et regum 1357–1378'
– digital pre-publication of documents by Charles IV by the MGH *
Aleksandra Filipek-Misiak, Karol IV Luksemburski jako ideał władcy w Catalogus abbatum Saganensium Ludolfa z Żagania, In: Historie – Otázky – Problémy, 7 (2015), z. 1, p. 76-89
{{DEFAULTSORT:Charles 04, Holy Roman Emperor 1316 births 1378 deaths 14th-century Holy Roman Emperors Anti-kings Medieval kings of Bohemia 14th-century Bohemian people House of Luxembourg Counts of Luxembourg Prince-electors of Brandenburg Czech people of Luxembourgian descent Czech expatriates in France Czech people of French descent Nobility from Prague Burials at St. Vitus Cathedral 14th-century Luxembourgian people Czech Roman Catholics
King of Bohemia
The Duchy of Bohemia was established in 870 and raised to the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1198. Several Bohemian monarchs ruled as non-hereditary kings beforehand, first gaining the title in 1085. From 1004 to 1806, Bohemia was part of the Holy Roman ...
to become Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
. He was a member of the House of Luxembourg
The House of Luxembourg ( lb, D'Lëtzebuerger Haus; french: Maison de Luxembourg; german: Haus Luxemburg) or Luxembourg dynasty was a royal family of the Holy Roman Empire in the Late Middle Ages, whose members between 1308 and 1437 ruled as king ...
from his father's side and the Bohemian House of Přemyslid
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condit ...
from his mother's side; he emphasized the latter due to his lifelong affinity for the Bohemian side of his inheritance, and also because his direct ancestors in the Přemyslid line included two saints.
He was the eldest son and heir of John of Bohemia
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of ...
, King of Bohemia and Count of Luxembourg
The territory of Luxembourg has been ruled successively by counts, dukes and grand dukes. It was part of the medieval Kingdom of Germany, and later the Holy Roman Empire until it became a sovereign state in 1815.
Counts of Luxembourg
House of A ...
, who died at the Battle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 in northern France between a French army commanded by King PhilipVI and an English army led by King EdwardIII. The French attacked the English while they were traversing northern France du ...
on 26 August 1346. His mother, Elizabeth, Queen of Bohemia
Elizabeth Stuart (19 August 159613 February 1662) was Electress of the Palatinate and briefly Queen of Bohemia as the wife of Frederick V of the Palatinate. Since her husband's reign in Bohemia lasted for just one winter, she is called the Wi ...
, was the sister of Wenceslaus III, King of Bohemia and Poland, the last of the male Přemyslid rulers of Bohemia. Charles inherited the County of Luxembourg
The County of Luxemburg (french: Luxembourg; lb, Lëtzebuerg) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It arose from medieval '' Lucilinburhuc'' ("Little Fortress") Castle in the present-day City of Luxembourg, purchased by Siegfried, Count of ...
from his father and was elected king of the Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia ( cs, České království),; la, link=no, Regnum Bohemiae sometimes in English literature referred to as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe, the predecessor of the modern Czec ...
. On 2 September 1347, Charles was crowned King of Bohemia.
On 11 July 1346, the prince-electors
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the prince ...
chose him as King of the Romans
King of the Romans ( la, Rex Romanorum; german: König der Römer) was the title used by the king of Germany following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German k ...
(''rex Romanorum'') in opposition to Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328.
Louis' election as king of Germany in ...
. Charles was crowned on 26 November 1346 in Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr r ...
. After his opponent died, he was re-elected in 1349 and crowned King of the Romans. In 1355, he was crowned King of Italy
King of Italy ( it, links=no, Re d'Italia; la, links=no, Rex Italiae) was the title given to the ruler of the Kingdom of Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The first to take the title was Odoacer, a barbarian military leader, ...
and Holy Roman Emperor. With his coronation as King of Burgundy
The following is a list of the kings of the two kingdoms of Burgundy, and a number of related political entities devolving from Carolingian machinations over family relations.
Kings of the Burgundians
* Gebicca (late 4th century – c. 407 ...
in 1365, he became the personal ruler of all the kingdoms of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
.
Having played a tremendous part in the political and cultural history of the Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia ( cs, České království),; la, link=no, Regnum Bohemiae sometimes in English literature referred to as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe, the predecessor of the modern Czec ...
, he remains a very popular figure in the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
. The Golden Bull of 1356
The Golden Bull of 1356 (, , , , ) was a decree issued by the Imperial Diet at Nuremberg and Metz ( Diet of Metz, 1356/57) headed by the Emperor Charles IV which fixed, for a period of more than four hundred years, important aspects of the con ...
marked a structural change in the politics of the Holy Roman Empire. Several aspects of his legacy remain a contentious matter though. The image of Charles as a wise, pious, peace-loving king (partly constructed by Charles himself) has proved influential until this day, supported by several artistic or scholarly projects produced during Charles's reign or afterwards.
Life
Birth and childhood
Charles was born toJohn of Bohemia
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of ...
of the Luxembourg dynasty and Queen Elizabeth of Bohemia of the Bohemian Přemyslid dynasty
The Přemyslid dynasty or House of Přemyslid ( cs, Přemyslovci, german: Premysliden, pl, Przemyślidzi) was a Bohemian royal dynasty that reigned in the Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia and Margraviate of Moravia (9th century–130 ...
in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
. His maternal grandfather was the Bohemian King Wenceslaus II
Wenceslaus II Přemyslid ( cs, Václav II.; pl, Wacław II Czeski; 27 SeptemberK. Charvátová, ''Václav II. Král český a polský'', Prague 2007, p. 18. 1271 – 21 June 1305) was King of Bohemia (1278–1305), Duke of Cracow (1291–1 ...
. He chose the name Charles at his confirmation
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. For adults, it is an affirmation of belief. It involves laying on ...
in honor of his uncle, King Charles IV of France
Charles IV (18/19 June 1294 – 1 February 1328), called the Fair (''le Bel'') in France and the Bald (''el Calvo'') in Navarre, was last king of the direct line of the House of Capet, King of France and King of Navarre (as Charles I) from 132 ...
, at whose court he was resident for seven years.
Charles received French education and was literate and fluent in five languages: Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, French, and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
.
Italy and Moravia
In 1331, he gained some experience of warfare in Italy with his father. At the beginning of 1333, Charles went toLucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957.
Lucca is known as one o ...
(Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; it, Toscana ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of about 3.8 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence (''Firenze'').
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, art ...
) to consolidate his rule there. In an effort to defend the city, Charles founded the nearby fortress and the town of Montecarlo
Monte Carlo (; ; french: Monte-Carlo , or colloquially ''Monte-Carl'' ; lij, Munte Carlu ; ) is officially an administrative area of the Principality of Monaco, specifically the ward of Monte Carlo/Spélugues, where the Monte Carlo Casino is l ...
(Charles' Mountain).
From 1333, he administered the lands of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were a number of incorporated states in Central Europe during the medieval and early modern periods connected by feudal relations under the Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom of B ...
due to his father's frequent absence and deteriorating eyesight. In 1334, Charles was named Margrave of Moravia
The Margraviate of Moravia ( cs, Markrabství moravské; german: Markgrafschaft Mähren) was one of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown within the Holy Roman Empire existing from 1182 to 1918. It was officially administrated by a margrave in cooperat ...
, the traditional title for heirs to the throne. Two years later, he assumed the government of Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
on behalf of his brother, John Henry, and was soon actively involved in a struggle for the possession of this county.
King of the Romans
On 11 July 1346, in consequence of an alliance between his father andPope Clement VI
Pope Clement VI ( la, Clemens VI; 1291 – 6 December 1352), born Pierre Roger, was head of the Catholic Church from 7 May 1342 to his death in December 1352. He was the fourth Avignon pope. Clement reigned during the first visitation of the Bla ...
, relentless enemy of the emperor Louis IV, Charles was elected as Roman king in opposition to Louis by some of the prince-electors
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the prince ...
at Rhens
Rhens is a municipality in the district Mayen-Koblenz, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is situated on the left bank of the Rhine, approx. 10 km south of Koblenz.
Rhens was the seat of the former ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective munici ...
. As he had previously promised to be subservient to Clement, he made extensive concessions to the pope in 1347. Confirming the papacy in the possession of vast territories, he promised to annul the acts of Louis against Clement, to take no part in Italian affairs, and to defend and protect the church.
 Charles IV was in a very weak position in Germany. Owing to the terms of his election, he was derisively referred to as a "Priests' King" (''Pfaffenkönig''). Many bishops and nearly all of the
Charles IV was in a very weak position in Germany. Owing to the terms of his election, he was derisively referred to as a "Priests' King" (''Pfaffenkönig''). Many bishops and nearly all of the Imperial cities
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
remained loyal to Louis the Bavarian. Worse still, Charles backed the wrong side in the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
, losing his father and many of his best knights at the Battle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 in northern France between a French army commanded by King PhilipVI and an English army led by King EdwardIII. The French attacked the English while they were traversing northern France du ...
in August 1346, with Charles himself escaping from the field wounded.
Civil war in Germany was prevented, however, when Louis IV died on 11 October 1347, after suffering a stroke during a bear hunt. In January 1349, House of Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a German dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including Bavaria, the Palatinate, Holland and Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland), Denmark, Norway, Hungary (with Romania), Bohemia, the Electorate ...
partisans attempted to secure the election of Günther von Schwarzburg
Günther XXI von Schwarzburg (c. 1304 – 14 June 1349), disputed King of Germany, was a descendant of the counts of Schwarzburg.
Biography
Born as the younger son of Henry VII, Count of Schwarzburg-Blankenburg (c. 1267 - 1324) and his wife, ...
as king, but he attracted few supporters and was defeated by Charles at the siege of Eltville The siege of Eltville (or battle of Eltville) in May 1349 was the military engagement by which Charles IV secured the throne of the Holy Roman Empire against his rival, Günther of Schwarzburg. It was the third time a disputed succession in the Em ...
in May. Thereafter, Charles faced no direct threat to his claim to the Imperial throne.
Charles initially worked to secure his power base. Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
had remained untouched by the plague. Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
became his capital, and he rebuilt the city on the model of Paris, establishing the New Town
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
(''Nové Město''). In 1348, he founded the Charles University in Prague
Charles University ( cs, Univerzita Karlova, UK; la, Universitas Carolina; german: Karls-Universität), also known as Charles University in Prague or historically as the University of Prague ( la, Universitas Pragensis, links=no), is the oldest an ...
, which was later named after him and was the first university in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
. This served as a training ground for bureaucrats and lawyers. Soon Prague emerged as the intellectual and cultural center of Central Europe.
 Having made good use of the difficulties of his opponents, Charles was again elected in
Having made good use of the difficulties of his opponents, Charles was again elected in Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , "Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its na ...
on 17 June 1349 and re-crowned at Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th- ...
on 25 July 1349. He was soon the undisputed ruler of the Empire. Gifts or promises had won the support of the Rhenish and Swabia
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
n towns; a marriage alliance secured the friendship of the Habsburgs; and an alliance with Rudolf II of Bavaria, Count Palatine of the Rhine
The counts palatine of Lotharingia /counts palatine of the Rhine /electors of the Palatinate (german: Kurfürst von der Pfalz) ruled some part of Rhine area in the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire from 915 to 1803. The title was a kind ...
, was obtained when Charles, who had become a widower in 1348, married Rudolph's daughter Anna
Anna may refer to:
People Surname and given name
* Anna (name)
Mononym
* Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke
* Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773)
* Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century)
* Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 12 ...
.
In 1350, the king was visited at Prague by the Roman tribune Cola di Rienzo
Nicola Gabrini (1313 8 October 1354), commonly known as Cola di Rienzo () or Rienzi, was an Italian politician and leader, who styled himself as the "tribune of the Roman people".
Having advocated for the abolition of temporal papal power a ...
, who urged him to go to Italy, where the poet Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited w ...
and the citizens of Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
also implored his presence.Francesco Petrarca
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited w ...
''Epistolae familiares
''Epistolae familiares'' is the title of a collection of letters of Petrarch which he edited during his lifetime. He originally called the collection ''Epistolarum mearum ad diversos liber'' (''"a book of my letters to different people"'') but th ...
'' X.1, XII.1, XVIII.1; See also: E.H. Wilkins ''Life of Petrarch'' (Chicago, 1961) 97, 112, 134 resp. Turning a deaf ear to these entreaties, Charles kept Cola in prison for a year, and then handed him as a prisoner to Clement at Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
.
Outside Prague, Charles attempted to expand the Bohemian crown lands, using his imperial authority to acquire fiefs in Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, the Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (german: Oberpfalz, , ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, and is located in the east of Bavaria.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and numerous ponds and lakes ...
, and Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper Fr ...
. The latter regions comprised "New Bohemia", a string of possessions intended to link Bohemia with the Luxemburg territories in the Rhineland. The Bohemian estates, however, were not willing to support Charles in these ventures. When Charles sought to codify Bohemian law in the Maiestas Carolina The Maiestas Carolina was a legal code proposed by Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor in 1350 to govern Bohemia. It received its name not before 1617.
Based on previous legal customs and the Liber Augustalis of 1231, the aim of the code was to increase ...
of 1355, he met with sharp resistance. After that point, Charles found it expedient to scale back his efforts at centralization.
Holy Roman Emperor
 In 1354, Charles crossed the
In 1354, Charles crossed the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
without an army, received the Lombard crown in St. Ambrose Basilica, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, on 6 January 1355, and was crowned emperor at Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
by a cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
on April 5th of the same year.František Palacký
František Palacký (; June 17, 1798 – May 26, 1876) was a Czech historian and politician, the most influential person of the Czech National Revival, called "Father of the Nation".
Life
František Palacký was born on June 17, 1798 at Hodslavi ...
. ''Dějiny národu českého v Čechách i v Moravě'', books VIII and IX His sole object appears to have been to obtain the Imperial crown in peace, in accordance with a promise previously made to Pope Clement. He only remained in the city for a few hours, in spite of the expressed wishes of the Roman people. Having virtually abandoned all the Imperial rights in Italy, the emperor re-crossed the Alps, pursued by the scornful words of Petrarch, but laden with considerable wealth.Francesco Petrarca
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited w ...
, ''Epistolae familiares
''Epistolae familiares'' is the title of a collection of letters of Petrarch which he edited during his lifetime. He originally called the collection ''Epistolarum mearum ad diversos liber'' (''"a book of my letters to different people"'') but th ...
'' XIX.12; see also E. H. Wilkins, ''Life of Petrarch'' (Chicago, 1961), p. 147 On his return, Charles was occupied with the administration of the Empire, then just recovering from the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
, and in 1356, he promulgated the famous Golden Bull
A golden bull or chrysobull was a decree issued by Byzantine Emperors and later by monarchs in Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, most notably by the Holy Roman Emperors. The term was originally coined for the golden seal (a ''bull ...
to regulate the election of the king.
 Having given
Having given Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The me ...
to one brother, John Henry, and erected the county of Luxembourg
The County of Luxemburg (french: Luxembourg; lb, Lëtzebuerg) was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It arose from medieval '' Lucilinburhuc'' ("Little Fortress") Castle in the present-day City of Luxembourg, purchased by Siegfried, Count of ...
into a duchy for another, Wenceslaus
Wenceslaus, Wenceslas, Wenzeslaus and Wenzslaus (and other similar names) are Latinized forms of the Czech name Václav. The other language versions of the name are german: Wenzel, pl, Wacław, Więcesław, Wieńczysław, es, Wenceslao, russian: ...
, he was unremitting in his efforts to secure other territories as compensation and to strengthen the Bohemian monarchy. To this end he purchased part of the upper Palatinate of the Rhine in 1353, and in 1367 annexed Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; szl, Dolnŏ Łużyca; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the sou ...
to Bohemia and bought numerous estates in various parts of Germany. On the death of Meinhard, Duke of Upper Bavaria and Count of Tyrol
The (Princely) County of Tyrol was an estate of the Holy Roman Empire established about 1140. After 1253, it was ruled by the House of Gorizia and from 1363 by the House of Habsburg. In 1804, the County of Tyrol, unified with the secularised pr ...
, in 1363, Upper Bavaria
Upper Bavaria (german: Oberbayern, ; ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany.
Geography
Upper Bavaria is located in the southern portion of Bavaria, and is centered on the city of Munich, both state capital and seat o ...
was claimed by the sons of the emperor Louis IV, and Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
by Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria. Both claims were admitted by Charles on the understanding that if these families died out both territories should pass to the House of Luxembourg
The House of Luxembourg ( lb, D'Lëtzebuerger Haus; french: Maison de Luxembourg; german: Haus Luxemburg) or Luxembourg dynasty was a royal family of the Holy Roman Empire in the Late Middle Ages, whose members between 1308 and 1437 ruled as king ...
. At about the same time, he was promised the succession to the Margravate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out o ...
, which he actually obtained for his son Wenceslaus in 1373.
Casimir III of Poland
Casimir III the Great ( pl, Kazimierz III Wielki; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, and fought to retain the title in the Galicia-Volhynia Wars. He wa ...
and Louis I of Hungary
Louis I, also Louis the Great ( hu, Nagy Lajos; hr, Ludovik Veliki; sk, Ľudovít Veľký) or Louis the Hungarian ( pl, Ludwik Węgierski; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370 ...
entered a conspiracy against Charles and managed to persuade Otto V of Bavaria to join. After the repeal of the estate contract by margrave Otto, in early July 1371, Charles IV declared hostilities and invaded Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out o ...
; after two years of conflict, in 1373 Brandenburg became part of the Czech lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands ( cs, České země ) are the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia. Together the three have formed the Czech part of Czechoslovakia since 1918, the Czech Socialist Republic since 1 ...
. This was when he gave the order to measure his new territory, its villages, people, and income. This was recorded in the Landbuch of Charles IV, which was finished in 1375. Many villages were mentioned for the first time in this book, so it can provide information on how old they are. He also gained a considerable portion of Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
n territory, partly by inheritance through his third wife, Anna von Schweidnitz
Anna of Schweidnitz ( Świdnica) (also known as Anne or Anna of Świdnica, cs, Anna Svídnická, pl, Anna Świdnicka, german: Anna von Schweidnitz und Jauer) ( Świdnica, 1339 – 11 July 1362 in Prague) was Queen of Bohemia, German Queen, an ...
, daughter of Henry II, Duke of Świdnica
Henry II of Świdnica, ( pl, Henryk II Świdnicki, cs, Jindřich Svídnický, german: Heinrich II. von Schweidnitz; – ), was a Duke of Świdnica from 1326 until his death (with his brother as co-ruler).
He was the second and younger son of Du ...
and Catherine of Hungary. In 1365, Charles visited Pope Urban V at Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
and undertook to escort him to Rome; on the same occasion he was crowned King of Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
at Arles
Arles (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Arle ; Classical la, Arelate) is a coastal city and commune in the South of France, a subprefecture in the Bouches-du-Rhône department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, in the former province of ...
.
His second journey to Italy took place in 1368 when he had a meeting with Pope Urban V at Viterbo
Viterbo (; Viterbese: ; lat-med, Viterbium) is a city and ''comune'' in the Lazio region of central Italy, the capital of the province of Viterbo.
It conquered and absorbed the neighboring town of Ferento (see Ferentium) in its early history. ...
, was besieged in his palace at Siena
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centuri ...
, and left the country before the end of 1369. During his later years, the emperor took little part in German affairs beyond securing the election of his son Wenceslaus as king of the Romans in 1376, and negotiating a peace between the Swabian League of Cities
The Swabian League of Cities (German: ''Schwäbischer Städtebund'') was a primarily military alliance between a number of free imperial cities in and around the area now defined as south-western Germany. Its objective was the maintenance of th ...
and some nobles in 1378. After dividing his lands between his three sons and his nephews, he died in November 1378 at Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
, where he was buried, and where a statue was erected to his memory in 1848.
Charles IV suffered from gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensit ...
(metabolic arthritis), a painful disease quite common in that time.
Legacy
Evaluation
The reign of Charles IV was characterized by a transformation in the nature of the Empire and is remembered as theGolden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the ''Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages of Man, Ages, Gold being the first and the one during ...
of Bohemia. He promulgated the Golden Bull of 1356
The Golden Bull of 1356 (, , , , ) was a decree issued by the Imperial Diet at Nuremberg and Metz ( Diet of Metz, 1356/57) headed by the Emperor Charles IV which fixed, for a period of more than four hundred years, important aspects of the con ...
whereby the succession to the imperial title was laid down, which held for the next four centuries.
He also organized the states of the empire into peace-keeping confederations
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
. In these, the Imperial cities figured prominently. The Swabian Landfriede confederation of 1370 was made up almost entirely of Imperial Cities
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
. At the same time, the leagues were organized and led by the crown and its agents. As with the electors, the cities that served in these leagues were given privileges to aid in their efforts to keep the peace.
He assured his dominance over the eastern borders of the Empire through succession treaties with the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s and the purchase of Brandenburg. He also claimed imperial lordship over the crusader states of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
and Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
.
In 2005 Charles IV ranked the first in the TV show ''Největší Čech
''Největší Čech'' (''The Greatest Czech'') is the Czech spin-off of the BBC ''Greatest Britons'' show; a television poll of the populace to name the greatest Czech in history. The series was broadcast by the national public-service broadcast ...
'', the Czech spin-off of the BBC ''Greatest Britons'' show.
Patronage of culture and the arts

Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
became the capital of the Holy Roman Empire during the reign of Charles IV. The name of the royal founder and patron remains on many monuments and institutions, for example Charles University
)
, image_name = Carolinum_Logo.svg
, image_size = 200px
, established =
, type = Public, Ancient
, budget = 8.9 billion CZK
, rector = Milena Králíčková
, faculty = 4,057
, administrative_staff = 4,026
, students = 51,438
, undergr ...
, Charles Bridge
Charles Bridge ( cs, Karlův most ) is a medieval stone arch bridge that crosses the Vltava river in Prague, Czech Republic. Its construction started in 1357 under the auspices of King Charles IV, and finished in the early 15th century.; The ...
, Charles Square
Charles Square ( cs, Karlovo náměstí) is a city square in the New Town of Prague, Czech Republic. At roughly 80,550 m² it is one of the largest squares in the world and was the largest town square of the medieval Europe. Founded in 1348 as th ...
. High Gothic
High Gothic is a particularly refined and imposing style of Gothic architecture that appeared in northern France from about 1195 until 1250. Notable examples include Chartres Cathedral, Reims Cathedral, Amiens Cathedral, Beauvais Cathedral, and ...
Prague Castle
Prague Castle ( cs, Pražský hrad; ) is a castle complex in Prague 1 Municipality within Prague, Czech Republic, built in the 9th century. It is the official office of the President of the Czech Republic. The castle was a seat of power for kin ...
and part of the cathedral of Saint Vitus by Peter Parler
Peter Parler (german: Peter von Gemünd, cs, Petr Parléř, la, Petrus de Gemunden in Suevia; 1333 – 13 July 1399) was a German-Bohemian architect and sculptor from the Parler family of master builders. Along with his father, Heinrich Parler, ...
were also built under his patronage. Finally, the first flowering of manuscript painting in Prague dates from Charles's reign. In the present Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
, he is still regarded as ''Pater Patriae
''Pater Patriae'' (plural ''Patres Patriae''), also seen as ''Parens Patriae'', is a Latin honorific meaning "Father of the Country", or more literally, "Father of the Fatherland". It is also used of U.S. President George Washington, the Swed ...
'' ( father of the country or ''otec vlasti''), a title first coined by Adalbertus Ranconis de Ericinio at his funeral.
Charles also had strong ties to Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
, staying within its city walls 52 times and thereby strengthening its reputation amongst German cities. Charles was the patron of the Nuremberg Frauenkirche
The Frauenkirche ("Church of Our Lady") is a church in Nuremberg, Germany. It stands on the eastern side of the main market. An example of brick Gothic architecture, it was built on the initiative of Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor between 1352 an ...
, built between 1352 and 1362 (the architect was likely Peter Parler
Peter Parler (german: Peter von Gemünd, cs, Petr Parléř, la, Petrus de Gemunden in Suevia; 1333 – 13 July 1399) was a German-Bohemian architect and sculptor from the Parler family of master builders. Along with his father, Heinrich Parler, ...
), where the imperial court worshipped during its stays in Nuremberg.
Charles's imperial policy was focused on the dynastic sphere and abandoned the lofty ideal of the Empire as a universal monarchy of Christendom. In 1353, he granted the Duchy of Luxembourg
The Duchy of Luxemburg ( nl, Luxemburg; french: Luxembourg; german: Luxemburg; lb, Lëtzebuerg) was a state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg, now Duke of Limburg, becam ...
to his half-brother, Wenceslaus
Wenceslaus, Wenceslas, Wenzeslaus and Wenzslaus (and other similar names) are Latinized forms of the Czech name Václav. The other language versions of the name are german: Wenzel, pl, Wacław, Więcesław, Wieńczysław, es, Wenceslao, russian: ...
. He concentrated his energies chiefly on the economic and intellectual development of Bohemia, where he founded the university in 1348 and encouraged the early humanists. He corresponded with Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited w ...
and invited him to visit the royal residence in Prague, whilst the Italian hoped – to no avail – to see Charles move his residence to Rome and reawaken tradition of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
.
Charles's sister Bona married the eldest son of Philip VI of France, the future John II of France, in 1335. Thus, Charles was the maternal uncle of Charles V of France, who solicited his relative's advice at Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand E ...
in 1356 during the Parisian Revolt
The Jacquerie () was a popular revolt by peasants that took place in northern France in the early summer of 1358 during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt was centred in the valley of the Oise north of Paris and was suppressed after a few wee ...
. This family connection was celebrated publicly when Charles made a solemn visit to his nephew in 1378, just months before his death. A detailed account of the occasion, enriched by many splendid miniatures, can be found in Charles V's copy of the ''Grandes Chroniques de France
The ''Grandes Chroniques de France'' is a vernacular royal compilation of the history of France, most manuscripts of which are luxury copies that are heavily illuminated. Copies were produced between the thirteenth and fifteenth centuries, the ...
''.
Castles
Castles built or established by Charles IV:/ref> *
Karlštejn
Karlštejn Castle ( cs, hrad Karlštejn; german: Burg Karlstein) is a large Gothic castle founded in 1348 by Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor-elect and King of Bohemia. The castle served as a place for safekeeping the Imperial Regalia as well as ...
, 1348–1355 in Central Bohemian Region
The Central Bohemian Region ( cz, Středočeský kraj, german: Mittelböhmische Region) is an administrative unit ( cz, kraj) of the Czech Republic, located in the central part of its historical region of Bohemia. Its administrative centre is in ...
for safekeeping the Imperial Regalia
The Imperial Regalia, also called Imperial Insignia (in German ''Reichskleinodien'', ''Reichsinsignien'' or ''Reichsschatz''), are regalia of the Holy Roman Emperor. The most important parts are the Crown, the Imperial orb, the Imperial sce ...
, especially the Imperial Crown of the Holy Roman Empire
The Imperial Crown of the Holy Roman Empire (german: Reichskrone), a hoop crown (german: Bügelkrone) with a characteristic octagonal shape, was the coronation crown of the Holy Roman Emperor, probably from the late 10th century until the dissolut ...
(later the Czech Crown Jewels
The Bohemian crown jewels, also called the Czech crown jewels ( cs, české korunovační klenoty), include the Crown of Saint Wenceslas (''Svatováclavská koruna''), the royal orb and sceptre, the coronation vestments of the Kings of Bohemia, ...
were also kept there)
* Kašperk (Karlsberg), 1356 in Kašperské Hory
Kašperské Hory (; german: Bergreichenstein) is a town in Klatovy District in the Plzeň Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 1,400 inhabitants. It is known as a ski resort. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an ur ...
in Plzeň Region
Plzeň Region ( cs, Plzeňský kraj; german: Pilsner Region) is an administrative unit (''kraj'') in the western part of Bohemia in the Czech Republic. It is named after its capital Plzeň (English, german: Pilsen). In terms of area, Plzeň Reg ...
* Lauf (Wenzelsburg) – built on the way connecting Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
and Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
in Bohemian Palatinate
The Bohemian Palatinate ( cs, Česká Falc) or Bohemian Upper Palatinate (german: Böhmische Oberpfalz), since the 19th century also called New Bohemia ( cs, Nové Čechy, german: Neuböhmen), is a historical area in the northeast of present-day B ...
, inside survived 112 coats of arms of the Bohemian Kingdom
* Montecarlo
Monte Carlo (; ; french: Monte-Carlo , or colloquially ''Monte-Carl'' ; lij, Munte Carlu ; ) is officially an administrative area of the Principality of Monaco, specifically the ward of Monte Carlo/Spélugues, where the Monte Carlo Casino is l ...
in Italy
* Radyně (Karlskrone) – around 1360 in Plzeň Region
* Hrádek u Purkarce (Karlshaus) – around 1357
* Tepenec (Twingenberg, Karlsburg) in Jívová
Jívová (german: Giebau) is a municipality and village in Olomouc District in the Olomouc Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 600 inhabitants.
Jívová lies approximately north-east of Olomouc and east of Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Pra ...
in Olomouc Region
Olomouc Region ( cs, Olomoucký kraj; , ; pl, Kraj ołomuniecki) is an administrative unit ( cs, kraj) of the Czech Republic, located in the north-western and central part of its historical region of Moravia (''Morava'') and in a small part of t ...
* Karlsfried
Places named after Charles IV
; Czech Republic *Karlovy Vary
Karlovy Vary (; german: Karlsbad, formerly also spelled ''Carlsbad'' in English) is a spa town, spa city in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 46,000 inhabitants. It lies on the confluence of the rivers Ohře and Teplá. ...
, a spa city
* Karlštejn
Karlštejn Castle ( cs, hrad Karlštejn; german: Burg Karlstein) is a large Gothic castle founded in 1348 by Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor-elect and King of Bohemia. The castle served as a place for safekeeping the Imperial Regalia as well as ...
, a town beyond the eponymous castle
* Charles Bridge
Charles Bridge ( cs, Karlův most ) is a medieval stone arch bridge that crosses the Vltava river in Prague, Czech Republic. Its construction started in 1357 under the auspices of King Charles IV, and finished in the early 15th century.; The ...
(''Karlův most''), Prague
* Charles University
)
, image_name = Carolinum_Logo.svg
, image_size = 200px
, established =
, type = Public, Ancient
, budget = 8.9 billion CZK
, rector = Milena Králíčková
, faculty = 4,057
, administrative_staff = 4,026
, students = 51,438
, undergr ...
(''Univerzita Karlova''), Prague
* Multiple squares – Charles Square
Charles Square ( cs, Karlovo náměstí) is a city square in the New Town of Prague, Czech Republic. At roughly 80,550 m² it is one of the largest squares in the world and was the largest town square of the medieval Europe. Founded in 1348 as th ...
(''Karlovo náměstí'') in Prague and others, for example in Brno
Brno ( , ; german: Brünn ) is a city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava and Svratka rivers, Brno has about 380,000 inhabitants, making it the second-largest city in the Czech Republic ...
, Kolín
Kolín (; german: Kolin, Neu Kolin, Collin) is a town in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 32,000 inhabitants. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument reservation.
Administra ...
, Mělník
Mělník (; german: Melnik) is a town in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 19,000 inhabitants. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument zone.
Mělník lies in one of the most im ...
etc.
* Multiple streets
; Italy
* Montecarlo
Monte Carlo (; ; french: Monte-Carlo , or colloquially ''Monte-Carl'' ; lij, Munte Carlu ; ) is officially an administrative area of the Principality of Monaco, specifically the ward of Monte Carlo/Spélugues, where the Monte Carlo Casino is l ...
(Charles's Mountain), a municipality
Other
 * The 100-
* The 100-Czech koruna
The koruna, or crown, (sign: Kč; code: CZK, cs, koruna česká) has been the currency of the Czech Republic since 1993. The koruna is one of the European Union's 9 currencies, and the Czech Republic is legally bound to adopt the euro currenc ...
banknote
* 16951 Carolus Quartus, an asteroid
Family
Genealogy
Marriages and children
 Charles was married four times. His first wife was
Charles was married four times. His first wife was Blanche of Valois
Blanche of Valois (baptised ''Marguerite''; 1317–1348) was Queen of Germany and Bohemia by her marriage to King and later Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV. She was the youngest daughter of Charles of Valois and his third wife Mahaut of Châtillo ...
(1316–1348), daughter of Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
, Count of Valois
The Valois ( , also , ; originally ''Pagus Valensis'') was a region in the valley of the Oise river in Picardy in the north of France. It was a fief in West Francia and subsequently the Kingdom of France until its counts furnished a line of king ...
, and a half-sister of King Philip VI of France. They had three children:
* son (b. 1334), died young
* Margaret of Bohemia, Queen of Hungary
Margaret of Bohemia (24 May 1335 – 1349, before October), also known as Margaret of Luxembourg, was a Queen consort of Hungary by her marriage to Louis I of Hungary. She was the second child of Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor by his first wif ...
(1335–1349); married King Louis I of Hungary.
* Catherine of Bohemia
Catherine of Bohemia ( cs, Kateřina Lucemburská, german: Katharina von Böhmen; 19 August 1342 – 26 April 1395) also known as Catherine of Luxembourg was Electress of Brandenburg, the second daughter of Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV ...
(1342–1395); married Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria
Rudolf IV (1 November 1339 – 27 July 1365), also called Rudolf the Founder (german: der Stifter), was a scion of the House of Habsburg who ruled as duke of Austria (self-proclaimed archduke), Styria and Carinthia from 1358, as well as count ...
and Otto V, Duke of Bavaria and Elector of Brandenburg.
He secondly married Anna of Bavaria
Anne of Bavaria (or of the Palatinate; ; 26 September 1329 – 2 February 1353) was Queen of Bohemia by marriage to Charles of Luxembourg. She was the daughter of Rudolf II, Count Palatine of the Rhine, and Anna, daughter of Otto III ...
, (1329–1353), daughter of Rudolf II, Count Palatine of the Rhine; they had one son:
* Wenceslaus (1350–1351).
His third wife was Anna von Schweidnitz
Anna of Schweidnitz ( Świdnica) (also known as Anne or Anna of Świdnica, cs, Anna Svídnická, pl, Anna Świdnicka, german: Anna von Schweidnitz und Jauer) ( Świdnica, 1339 – 11 July 1362 in Prague) was Queen of Bohemia, German Queen, an ...
, (1339–1362), daughter of Henry II, Duke of Świdnica and Katharina of Anjou (daughter of Charles I Robert, King of Hungary), by whom he had three children:
* Elisabeth of Bohemia (19 April 1358 – 4 September 1373); married Albert III, Duke of Austria at the very young age of 8 and died at the age of 15, they had no children.
* Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia
Wenceslaus IV (also ''Wenceslas''; cs, Václav; german: Wenzel, nicknamed "the Idle"; 26 February 136116 August 1419), also known as Wenceslaus of Luxembourg, was King of Bohemia from 1378 until his death and King of Germany from 1376 until he w ...
(1361–1419); later elected King of Germany (formally King of the Romans) and on his father's death, became King of Bohemia (as Wenceslaus IV) and Emperor-elect of the Holy Roman Empire; married firstly to Joanna of Bavaria
Joanna of Bavaria (c. 1362 – 31 December 1386), a member of the House of Wittelsbach, was German queen from 1376 and Queen of Bohemia from 1378 until her death, by her marriage with the Luxembourg king Wenceslaus.
Life
Presumably born in The ...
in 1370 and secondly to Sophia of Bavaria in 1389.
* son (born and died 11 July 1362).
His fourth wife was Elizabeth of Pomerania
Elizabeth of Pomerania ( pl, Elżbieta pomorska, cs, Eliška Pomořanská; – 15 April 1393) was the fourth and final wife of Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor and King of Bohemia.
Life
Elizabeth was the daughter of Bogislaw V, Duk ...
, (1345 or 1347 – 1393), daughter of Bogislaw V, Duke of Pomerania and Elisabeth of Poland
Elizabeth of Poland ( hu, Erzsébet, pl, Elżbieta; 1305 – 29 December 1380) was Queen of Hungary by marriage to Charles I of Hungary, and regent of Poland from 1370 to 1376 during the reign of her son Louis I.
Life Early life
She was a memb ...
who was the daughter of King Casimir III of Poland. They had six children:
* Anne of Bohemia, Queen of England (1366–1394); married King Richard II of England
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father die ...
* Sigismund of Bohemia
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 – 9 December 1437) was a monarch as King of Hungary and Croatia (''jure uxoris'') from 1387, King of Germany from 1410, King of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in 1 ...
(1368–1437); later became Holy Roman Emperor, was King of Bohemia, Margrave of Brandenburg
This article lists the Margraves and Electors of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg during the period of time that Brandenburg was a constituent state of the Holy Roman Empire.
The Mark, or ''March'', of Brandenburg was one of the primary c ...
, and also King of Hungary
The King of Hungary ( hu, magyar király) was the ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Apostoli Magyar Király'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 ...
through his first marriage to Mary, Queen of Hungary
Mary, also known as Maria of Anjou (, , ; 137117 May 1395), reigned as Queen of Hungary and Croatia (officially 'king') between 1382 and 1385, and from 1386 until her death. She was the daughter of Louis the Great, King of Hungary and Poland, ...
in 1385. His second marriage was to Barbara of Cilli
Barbara of Cilli or Barbara of Celje ( Hungarian: ''Cillei Borbála'', German: ''Barbara von Cilli,'' Slovenian and Croatian'': Barbara Celjska,'' 1392 – 11 July 1451), was the Holy Roman Empress and Queen of Hungary and Bohemia by marriag ...
, the daughter and youngest child of Herman II, Count of Celje
Hermann II ( sl, Herman; early 1360s – 13 October 1435), Count of Celje, was a Styrian prince and magnate, most notable as the faithful supporter and father-in-law of the Hungarian king and Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund of Luxembourg. Hermann ...
, in 1405/1408.
* John of Bohemia
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of ...
(1370–1396); later Margrave of Moravia
The Margraviate of Moravia ( cs, Markrabství moravské; german: Markgrafschaft Mähren) was one of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown within the Holy Roman Empire existing from 1182 to 1918. It was officially administrated by a margrave in cooperat ...
and Duke of Görlitz
Görlitz (; pl, Zgorzelec, hsb, Zhorjelc, cz, Zhořelec, :de:Ostlausitzer Mundart, East Lusatian dialect: ''Gerlz'', ''Gerltz'', ''Gerltsch'') is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is located on the Lusatian Neisse River, and ...
; married Richardis Catherine of Sweden Richardis Catherine of Mecklenburg (1370 or 1372 in Sweden – 1400), was a Princess of Sweden and Mecklenburg, and by marriage a Margravine consort of Moravia and Duchess consort of Görlitz (Lusatia), daughter-in-law of the Holy German Emperor.Chr ...
, the daughter of Albert, King of Sweden
Albert (german: Albrecht, sv, Albrekt av Mecklenburg; c. 1338 – 1 April 1412) was King of Sweden from 1364 to 1389 and Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin from 1384 to 1412.
Background
He was the second son of Duke Albert II of Mecklenburg and ...
. His only daughter and heiress Elisabeth of Görlitz
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sc ...
was Duchess of Luxembourg.
* Charles (13 March 1372 – 24 July 1373).
* Margaret of Bohemia, Burgravine of Nuremberg
Margaret is a female first name, derived via French () and Latin () from grc, μαργαρίτης () meaning "pearl". The Greek is borrowed from Persian.
Margaret has been an English name since the 11th century, and remained popular througho ...
(1373–1410); married John III, Burgrave of Nuremberg
John III of Nuremberg (c. 1369 – 11 June 1420 in Plassenburg), Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach from the House of Hohenzollern. He was elder son of Frederick V of Nuremberg and Elisabeth of Meissen.
Family and children
He was married c. 138 ...
.
* Henry (1377–1378)
References
Bibliography
* * *Further reading
* Charles IV (autobiography), edited by Balázs Nagy, Frank Schaer: ''Autobiography of Emperor Charles IV; And, His Legend of St. Wenceslas: Karoli IV Imperatoris Romanorum Vita Ab Eo Ipso Conscripta; Et, Hystoria Nova de Sancto Wenceslao Martyre'', Published by Central European University Press, 2001, , , 259 pagesbooks.google.com
*
External links
* *Entry in the ''Residenzen-Kommission''
Regesta Imperii
Publications on Charles IV.
in the OPAC of the Regesta Imperii
'Constitutiones et acta publica imperatorum et regum 1357–1378'
– digital pre-publication of documents by Charles IV by the MGH *
Aleksandra Filipek-Misiak, Karol IV Luksemburski jako ideał władcy w Catalogus abbatum Saganensium Ludolfa z Żagania, In: Historie – Otázky – Problémy, 7 (2015), z. 1, p. 76-89
{{DEFAULTSORT:Charles 04, Holy Roman Emperor 1316 births 1378 deaths 14th-century Holy Roman Emperors Anti-kings Medieval kings of Bohemia 14th-century Bohemian people House of Luxembourg Counts of Luxembourg Prince-electors of Brandenburg Czech people of Luxembourgian descent Czech expatriates in France Czech people of French descent Nobility from Prague Burials at St. Vitus Cathedral 14th-century Luxembourgian people Czech Roman Catholics